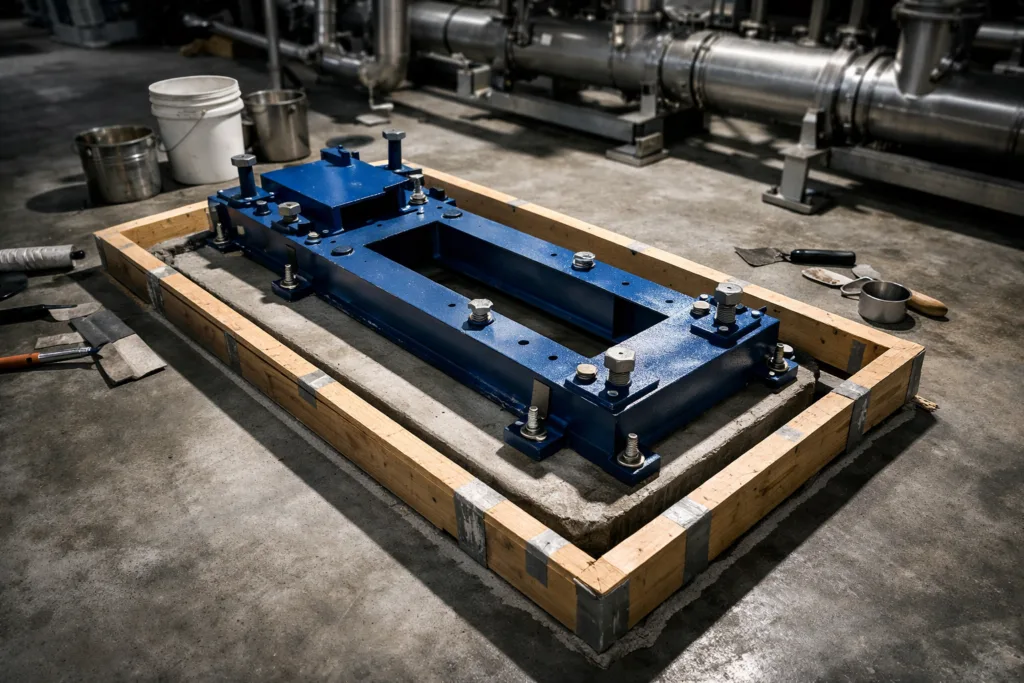
Introduction to API 610 Baseplate Grouting
Baseplate grouting is a vital step in ensuring the reliability and safety of pumps and rotating machinery, especially in industrial settings where the American Petroleum Institute’s API 610 standard sets the benchmark for quality. In this ultimate guide to API 610 baseplate grouting, we’ll examine why proper grouting is essential, what materials and techniques are best, and how you can overcome challenges to maximize pump performance and service life.
What Is API 610 Baseplate Grouting?
API 610 refers to a rigorous set of engineering requirements for centrifugal pumps in petroleum, petrochemical, and gas industries. One key section—baseplate grouting—dictates how grouts are used to secure the pump and motor baseplate to a concrete foundation. Following these guidelines ensures vibration control, misalignment prevention, and longer equipment life.
Why Baseplate Grouting Matters for Equipment Reliability
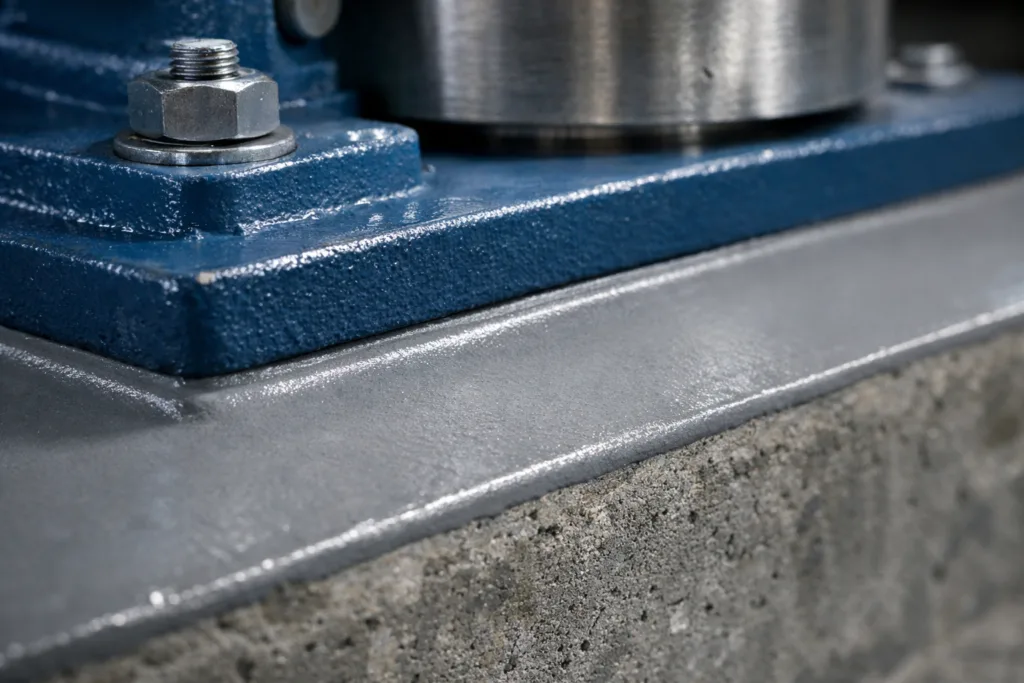
Proper grouting fills the gap between a baseplate and its foundation, ensuring support and load transfer. Skipping or rushing this process can result in vibration, misalignment, or even catastrophic pump failure. Even the best pumps underperform if the baseplate isn’t supported as per API 610.
Core Principles of API 610 Grouting
The API 610 standard emphasizes several core principles:
- Achieving a full contact area under the baseplate (Effective Bearing Area, or EBA)
- Using grouts with suitable compressive strength to handle pump loads
- Controlling shrinkage and flowability during installation
- Preventing voids and air pockets
- Managing expansion and contraction under real site conditions
Types of Grouting Materials: Cementitious vs Epoxy
Cement-based grouts are traditional but may crack or shrink over time. Epoxy grouts for heavy machinery, as recommended in API 610, offer higher strength, chemical resistance, and minimal shrinkage, making them ideal for demanding pump installations.
Key Properties of Epoxy Grout for API 610
- High compressive strength (often >90 MPa)
- Excellent bond to concrete and steel
- Low shrinkage and creep resistance
- Superior chemical resistance
- Appropriate working time (pot life) for installation size
Baseplate Grouting, API 610: Step-by-Step Overview
It’s crucial to follow a disciplined, stepwise approach for consistent results:
- Verify foundation quality and strength
- Clean and prepare surfaces (removing oil, dust, laitance)
- Install and secure formwork
- Mix grout carefully—respect batch size and pot life
- Pour or place grout—ensure all voids are filled
- Allow proper curing and avoid premature movement
Foundation Preparation: The Hidden Critical Factor
A clean, oil-free, roughened concrete surface ensures strong bonding and stress transfer. For contaminated foundations, sometimes epoxy concrete repair solutions are needed before grouting. Neglecting this step is a leading cause of real-world failures.
Mixing and Placing Epoxy Grout
Mixing ratios must be precise—too much resin leads to slow curing; too little, weak grout. ZDSpoxy site engineers stress always following manufacturer mixing procedures. Use a single batch when possible, and place the grout continuously to avoid cold joints.
Controlling Exotherm: Preventing Heat Damage
Epoxy grout can generate heat as it cures, especially in thick pours. Monitor pour thickness and ambient temperature, and consider pouring in layers if required. This prevents damage to the concrete and avoids premature curing.
Ensuring Complete Baseplate Contact (EBA 85% Rule)
API 610 recommends at least 85% Effective Bearing Area (EBA). Inspect after grouting to ensure all areas beneath the baseplate are fully supported by hardened grout. Skipping this verification is a common error leading to misalignment.
Challenging Site Conditions: Hot, Cold, & Wet Weather
Weather directly impacts grout performance. Low-temperature and high-temperature resistant formulations, such as ZDS-4120AB high-temperature epoxy grout, are formulated for reliability in challenging conditions. Always select product grades suited for real site climate.
Troubleshooting Epoxy Grouting Issues
- Voids under baseplate? – Occurs with rapid placement or unsealed forms; repair with injection grout.
- Poor bond? – Typically due to oily or dusty substrate; re-prep and regrout if needed.
- Curing problems? – Check mixing accuracies and environmental conditions.
- Cracks or surface blush? – May stem from excessive exotherm or low temperature; monitor pour rate and temperature recommendations.
Grout Formwork and Placement Techniques
Formwork must be leakproof and strong enough to hold the substantial load of fluid grout. Allow headspace for easy grout placement and bleed/air escape. Tilt the baseplate 1–2 degrees if possible for easier air expulsion.
Understanding the Curing Process
Curing is a chemical reaction—not just drying. Restrict baseplate movement and vibration until the grout reaches specified compressive strength. Protect from moisture or thermal shock during early cure.
Checking for Proper Grout Bond and Strength
Remove formwork carefully after the cure window to check for cracks, shrinkage, or debonding. Many sites use destructive or non-destructive tests to confirm bond and strength, as these are vital for long-term pump health.
Baseplate Grouting, API 610: Real Project Insights
On large, dynamic load pumps, ZDSpoxy researchers found that strict batch-size control and continuous, uninterrupted placement produced the least cracks and best alignment retention, echoing API 610 priorities.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Over-mixing and aerating the grout—leads to voids
- Ignoring pot life warnings—grout may start to gel inside the bucket
- Underestimating ambient temperature—hot weather speeds up reaction
- Skipping baseplate leveling before pouring grout—causes misalignment
Testing and Verifying API 610 Compliance
More than paperwork—real verification includes positive support, strength benchmarks, and visual/physical checks for voids, bond, and shrinkage. For critical installations, third-party testing is common.
Longevity Benefits: How Proper Grouting Maximizes Equipment Life
When grouting is done by the API 610 playbook, pumps remain aligned, vibration is reduced, and foundation cracks are rare. This means longer pump life, fewer unplanned shutdowns, and a lower total cost of ownership over decades.
Upgrading Old or Failing Grouts
Retrofitting with advanced grout—especially in upgrades—can correct long-standing foundation and alignment issues. Old cement grouts can often be replaced by high-performance epoxies for superior support.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Considerations
Always wear proper PPE (gloves, goggles, sleeves). Use grouts formulated to minimize VOCs and dust. Store and transport materials per manufacturer guidance, keeping out of direct sunlight and moisture.
Choosing Your Epoxy Grout for API 610 Applications
- Verify compressive and bond strength certifications
- Check flowability for tight clearances
- Select specialized formulations for unique needs, such as low-temperature (ZDS-3315AB low-temperature epoxy grout) or high-chemical resistance
Best Practices for Long-Term Pump Alignment
Rechecking alignment after grout cure is crucial. Thermal expansion, curing shrinkage, and torque values should always be monitored. Maintain detailed records for QA tracing and troubleshooting down the line.
How to Calculate Grout Quantities for Your Project
Measuring foundation voids and anchor requirements can be tricky. For precise planning, use resources like the Epoxy Grout Volume Calculator Project Quote to avoid waste or shortage and to plan work more efficiently.
Future Trends in API 610 Baseplate Grouting
The industry is shifting toward longer pot lives, lower exotherm, greener chemistry, and application-specific grouts for extremely harsh or sensitive environments. Monitoring technology is also emerging for verification of grout quality over time.
The Ultimate Guide to API 610 Baseplate Grouting
This article has equipped you with practical steps, materials expertise, and real-world strategies drawn from API 610 standards. By applying these best practices, you safeguard your pumps, reduce failures, and set up projects for lasting success.
Conclusion
Whether you’re designing a new pump installation or retrofitting an existing plant, API 610 baseplate grouting is crucial for achieving the performance, alignment, and reliability demanded by industry. The right material selection, preparation, and application discipline are non-negotiable. By focusing on these proven steps and regularly reviewing your results, your pump and foundation can withstand the test of time and workload. Keep advancing your knowledge as best practices in grouting continue to evolve with new technologies and standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the API 610 standard for baseplate grouting?
API 610 sets out design and installation rules for centrifugal pumps, including specifics for baseplate grouting to ensure equipment stability, proper alignment, and longevity in industrial plants.
Which grout types are recommended for API 610 pump baseplates?
Epoxy grouts, designed for non-shrink, high-strength performance, are ideal for meeting API 610 requirements, especially in harsh operational environments.
How long should epoxy grout cure before starting up pumps?
Most epoxy grouts require 24-48 hours for basic cure. Always check the specific product’s datasheet and ensure minimum compressive strength is reached before startup.
What are Effective Bearing Area (EBA) requirements?
API 610 suggests at least 85% EBA, meaning that 85% of the area under the baseplate must be in direct contact with solid grout after curing for best load transfer.
How can I avoid air pockets or voids under the baseplate?
Proper formwork, continuous placement, and use of flowable grout minimize the risk of trapped air and ensure full contact. Inspect grout after curing to detect and repair possible voids.
Does temperature impact epoxy baseplate grouting performance?
Yes. High temperatures can accelerate curing and shrink the working time, whereas cold climates may slow curing. Always choose a grout grade suitable for your operating conditions.
Related Reading
- 6 Insights on Load Transfer for Dynamic Machinery Grouting
- Why Creep Resistance Is Key for Lasting Pump Alignment
- Practical Crusher Foundation Grouting: Solutions & Application Tips
- Essential Guide: Choose Grout for Static vs. Dynamic Loads
- Master the 85% Bearing Area Rule for Safer Equipment Support